- Due:
Friday, February 10, 10pm
- Starter code:
See Assignment 4 on Canvas for the Github link.
- Submission:
Submit the contents of your repository via Gradescope. See Deliverables below for what to submit.
This is an individual assignment.
This assignment will take you through implementing data structures in C, working with arrays and pointers, and manually managing memory.
Warm-up Exercises
Before you start, you might find it helpful to review arrays, pointers, and dynamic memory allocation and run through these exercises marked EASY and MEDIUM from UC Riverside:
These are part of a C Tutorial.
Task 1: Queues
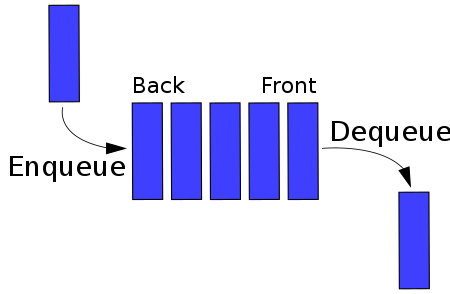
We have learned about the Linked List Data Structure in class and lab. Now let’s introduce another data structure, known as the ‘queue’.
A queue data structure is analogous to waiting in line at a grocery store. The first person to the checkout counter is served, followed by the next person, and then the next until the line is empty. A queue is what is known as a ‘first-in first-out’ (FIFO) data structure. Thus queues have a strict policy about how information is stored and accessed.
For this assignment, you are going to implement a specific implementation of a queue using the functions described in queue.h. This data structure is also called a circular queue (specifically, a ring buffer when the maximum storage size is fixed).
Circular Queue (Ring Buffer) implementation using an array.
A circular queue has a fixed sized, or maximum number of elements that it can hold. It is advantageous if we know how many elements are typically stored in a data structure. If we do not know, then a queue implemented using a linked is needed.
For more information on the Circular buffer, see here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Circular_buffer.
This animation below gives an idea about how the data structure ‘wraps’ around. Think about what mathematical operator has a wrap around behavior that could be useful in your implementation when enqueuing and dequeuing items in your queue (hint this operator will save you from writing many if-statements in your code!).
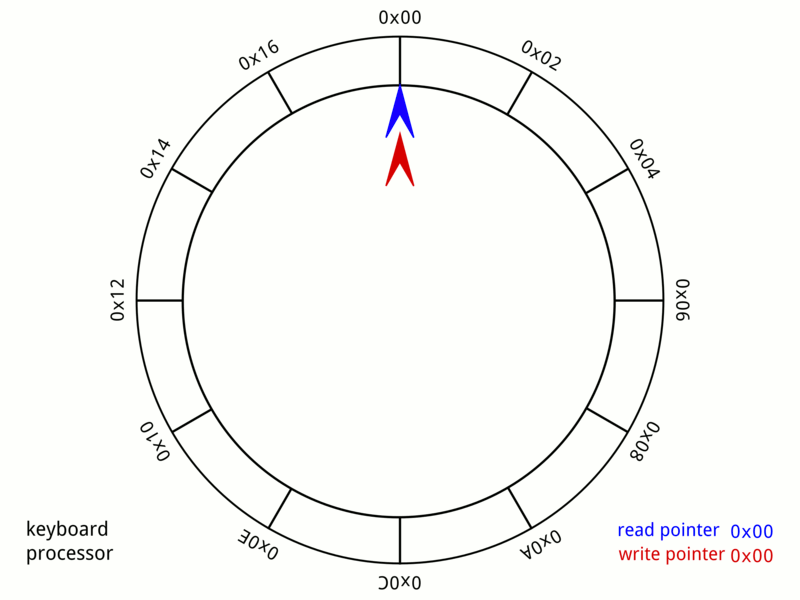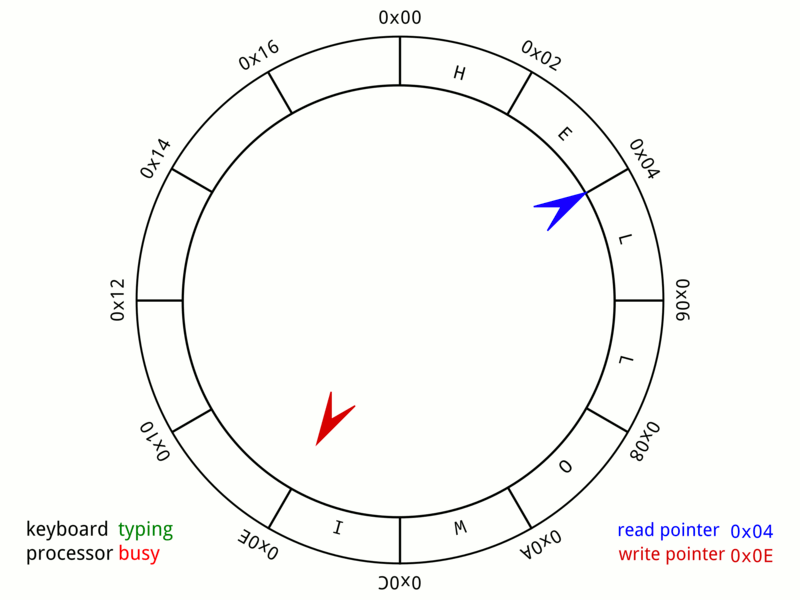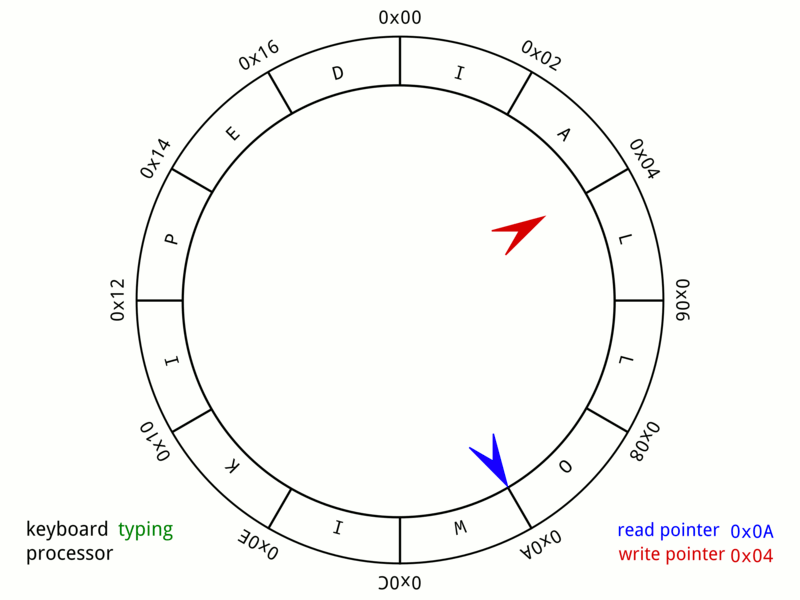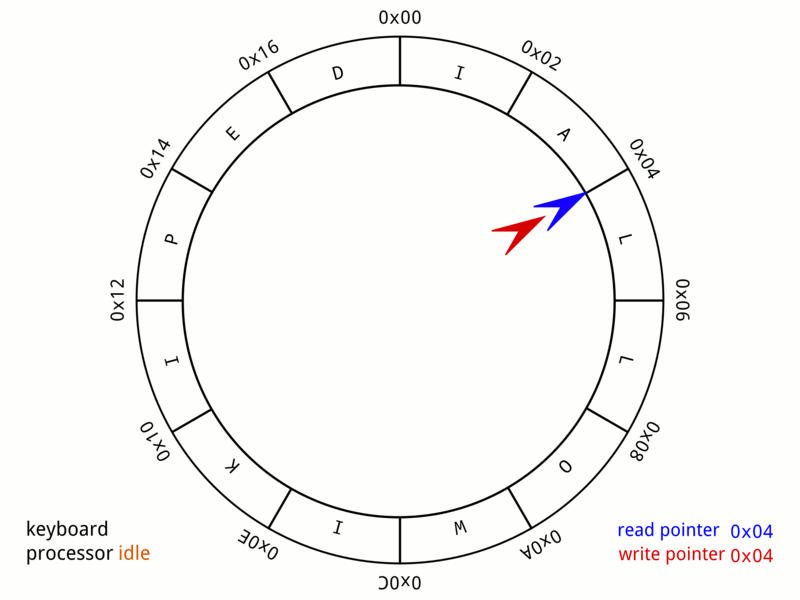
Your task is to implement, in queue.c the functions described in queue.h to create a working implementation of circular queue.
What is a file that ends in .h.
A file that ends in .h is known as a header file. A header file typically is a file that contains an ‘interface’ for a set of functions to perform some task. The actual implementation (i.e. the loops, if-statements, arrays, and tools that do work) are found in a .c file.
More information on header files: https://gcc.gnu.org/onlinedocs/cpp/Header-Files.html.
Unit Tests
A unit test is a standalone test that checks for the correctness of a specific use case in your code. In our case, we are testing if we have a working queue implementation. We provide a basic set of unit tests, written with the help of the μunit library (which is included with the starter files).
We provide a simple approach to writing unit tests with the starter code. For example:
MunitResult test1(const MunitParameter params[], void *data) {
queue_t* test1 = queue_new(1);
munit_assert_true(queue_empty(test1));
munit_assert_false(queue_full(test1));
queue_enqueue(test1, 42);
munit_assert_false(queue_empty(test1));
munit_assert_true(queue_full(test1));
munit_assert_long(queue_dequeue(test1), ==, 42);
munit_assert_true(queue_empty(test1));
munit_assert_false(queue_full(test1));
queue_delete(test1);
return MUNIT_OK;
}You may also consider writing some unit tests to test your implementation (In fact, we would strongly encourage you to do so). Note that you can include your unit tests in your submission, and we will have our own test suite. Some example tests we might come up with include:
- Fill a queue, empty the queue, and fill the queue again.
- Create an empty queue and attempt to add something to it.
- Make sure your queue does not overwrite any data.
- etc.
Provided Tests
You are provided a file called queue_test.c which you can compile separately and test your implementation of the queue functions specified in queue.h. These tests are a subset of what the autograder tests. Passing all the tests does not guarantee a perfect assignment, but it will give you some confidence your implementation is working and satisfies our requirements.
Task 2: Vectors or Resizable Arrays
Our circular queue in the previous section is implemented using a fixed size array. This has some benefits. There is O[1] access to any element. We can use array semantics to walk through how the data is stored. There are no pointers to traverse. However, because it uses a fixed size array, the size of the circular buffer can’t be increased.
On the other hand, linked lists are made up of individually allocated elements. The list can be of any size, but in most cases you need to traverse the pointers to find an element, i.e., access is not O[1]. For example, returning the 100th element of a linked list requires us to go through all 9d9 preceding items.
We’d like a construct that stores data and permits ~O[1] access that is also resizable during runtime.
The vector data structure
For this part of the assignment, you are to implement a vector, a data structure that is a resizable linear array. A vector, sometimes called a dynamic array, is a data structure similar to a Java’s ArrayList. It is also named vector in C++’s standard library. The vector will store strings (char *).
An example of a simple dynamic array would be to allocate an array of fixed size, usually larger than immediately required. The capacity of the dynamic array is the number of elements in the underlying array. The logical size of the dynamic array is the number of elements used in the underlying array. Logical size <= capacity.
The elements of the dynamic array are stored contiguously in the underlying array, until all space is consumed. When all space is consumed, and an additional element is to be added, then the underlying fixed-size array needs to be increased in size. Resizing is typically done by creating a new underlying array, copying the each value over to the new array, then deallocating the old array.
However, resizing by single element at a time is expensive, because there is potentially a significant amount of copying to only add a single new element. For resizing to be efficient, the new array is created to be the size of the old array times a growth factor: (old_array_size * VECT_GROWTH_FACTOR). If VECT_GROWTH_FACTOR = 2, the underlying fixed-size array would double in size everytime more space was needed. For more information, see our notes in vector.md in the starter code repository.
When a new string is added to the vector, a copy of the string should be made which is then stored. This means that the vector has ownership of its elements and when elements are removed, the memory they hold should also be removed. The vect_get function should return a const pointer to the vector’s copy of the string. The vect_get_copy function should return a copy of the string.
Your task is to implement the functions in vect.c to create a working implementation of a vector data structure.
Provided Tests
You are provided a file called vect_test.c which you can compile separately and test your implementation of your vector functions described in vect.h. These tests are a subset of the Gradescope autograder tests. Passing all the tests does not guarantee a perfect assignment, but it will give you some confidence your implementation is working.
Using the Provided Makefiles
Both queue and vector starter files include a Makefile to make your life easier. Here’s a quick overview of the possible targets:
make all- compile everythingmake test- compile and run tests in the respective unit test filemake valgrind- compile and run the tests through Valgrind - you should run this to check you are allocating and freeing memory correctly
A Few New Concepts
There are a few new concepts that we might not have covered in the lecture, which you will need to understand and use for this assignment.
Use assert to State (and Verify) Invariants
The assert statement helps check invariants that should be true about our code. We use it to state properties that we assume to hold at different parts of the code. If the assumption is broken, the program will fail early, with a message including the source file and line of the failing assert. We have provided some examples in the starter code, your job is to state additional assumptions you have. One example is to check that a pointer is not NULL before we use it:
int *numbers = malloc(5 * sizeof(int));
assert(numbers != NULL);
numbers[0] = 10;
//...See man 3 assert for more details.
const Means Something Should not Change
We use the const type modifier to tell the compiler that it should try to ensure that the given variable, argument, or return type should stay constant and not change. In particular, when used with strings (char *) it means that we need to make a copy of the string before we can do anything with it.
calloc and realloc
The functions calloc and realloc are close relatives of the malloc function. Briefly, calloc allocates a given number of elements of a given size and also resets the memory to 0. realloc is used to re-allocate memory, either to grow or to shrink the block we are using. It will also helpfully copy anything we had in the previous block to the new block. Learn how to use these two functions by studying their man pages: man 3 calloc / man 3 realloc.
Deliverables
- Task 1
Complete the queue implementation in the file
queue/queue.cand commit it to your repository.- Task 2
Complete the vector implementation in the file
vector/vect.cand commit it to your repository.
Do not include any executables, object files, or any other binary, intermediate or hidden files.
Finally, go to our Gradescope and submit a ZIP archive of your repository, which can be downloaded from Github. This step is required – committing to Github is not enough. Do not use Finder on macOS to compress your code for submission.
How will we grade
Your implementation will be graded by an autograder script on Gradescope, as well as by manual inspection aimed at checking correctness as well as the style and design of your code (comments, correct use of types, code layout, etc.)
- 40% Queue Implementation
- All required functions are implemented.
- No functions were renamed (but you may add any ‘helper’ functions if you deem necessary–e.g.
queue_print) - There are no memory leaks. Test your code using
valgrind. See thevalgrindtarget in the provided Makefile. - Your functions are free of compilation warnings, compilation errors, and runtime bugs
- 40% Vector Implementation
- All required functions are implemented
- No functions are renamed (but you may add any ‘helper’ functions if you deem necessary–e.g.
vect_print) - There are no memory leaks. Test your code using
valgrind. See thevalgrindtarget in the provided Makefile. - Your functions are free of compilation warnings, compilation errors, and runtime bugs
- 20% Style and Code Design
- Good source code structure (e.g., documented code, reasonable formatting and organization, …)
Resources to help
- http://www.learn-c.org/
- This is a nice interactive tutorial for learning C
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Queue_(abstract_data_type)
- Queue Data Type High level description
- http://www.cs.umd.edu/~nelson/classes/resources/cstyleguide/
- A very concise C style guide from UMD
Going Further
(An optional task to extend this assignment–not for bonus, but just for fun)
- Add additional functions like:
queue_peek- Returns the first value in the queuequeue_back- Returns the last value in the queuequeue_equals- Checks if two queues are equalvect_insert_at- Inserts an element into the vector at the given index, shifting subsequent elements to the rightvect_remove_at- Removes an element at the given index from the vector, shifting subsequent elements to the leftvect_sort- Sorts the vector in ascending order using your favorite sorting algorithm
- Investigate/Review more data structures on this webpage: https://www.cs.usfca.edu/~galles/visualization/Algorithms.html
- There are visuals for the linked list and array based queue here!
- Use them as a rough guide for the basic concepts. Make sure to follow the specifications for our assignment above.
- Some examples (Revisit this again in a few weeks)
Hints & Tips
Use man! Explore the manpages of
malloc,calloc,realloc,free,strncpy,strlen,assert, …Learn how to define constants in C
Write your own (unit) tests. Doing so will save you time in the long run, especially in conjunction with the debugger. In office hours, the instructors or the TAs may ask you to show how you tested code that fails.
Follow good coding practices. Make sure your function prototypes (signatures) are correct and always provide purpose statements. Add comments where appropriate to document your thinking, although strive to write self-documenting code.
Avoid producing “spaghetti code”. A mutli-branch
if-else if-elseor a multi-caseswitchshould be the only reason to go beyond 30-40 lines per function. Even so, the body of each branch/case should be at most 3-5 lines long.Use
valgrindwith--leak-check=fullto check you are managing memory properly.Avoid leaving extra
printfs in when submitting your code. Extra output will most likely result in point deductions by the autograder.